|
|
|
|
|
|
Usage
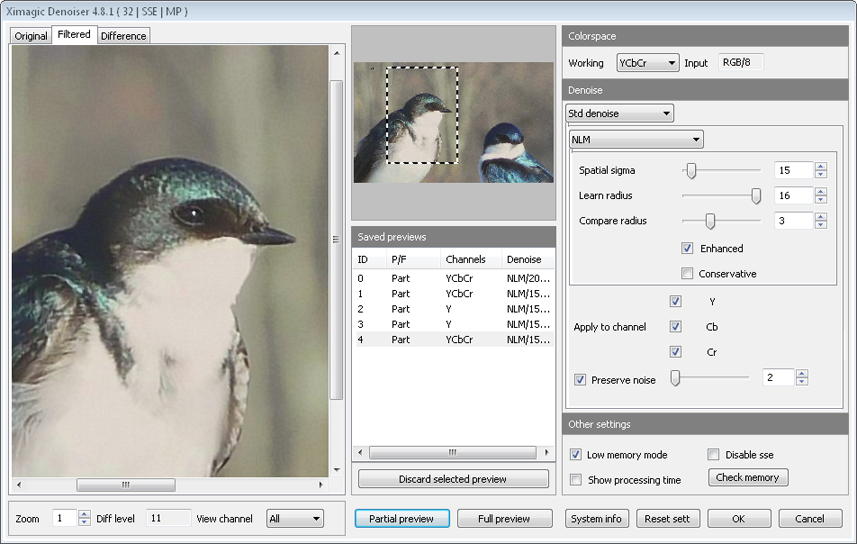
- Images
- Original image
- Transformed image
- DifferenceThis preview shows whether the denoising is removing only noise or also some information from the image. Less visible "ghost image" in the equalized error means better denoise. When the equalized noise shows a grid it is because the image was stored using jpeg format.
- Selection thumb & saved previews
- Selection thumb Shows the currently showing area of the image and allows to move it
- Saved Previews Each time a calculate preview is issued (partial or full) the result is temporarily saved. A saved preview can be viewed by selecting the corresponding line in the saved previews table.
- Discard selected preview Discard the saved preview currently selected in the table and showing in the images tabs
- Partial preview The partial preview button calculates only the preview of the area of the image inside the preview rectangle. The partial preview is only approximate for Wavelets (CWT/DWT) and Anisotropic diffusion.
- Full preview The full preview button calculates the preview of the whole image
- Colorspace
- Colorspace (RGB/YCbCr/CIELab) Usually, it is better to work on a colorspace which separate color from luminosity as YCbCr or CIELab.
- Denoise. The color denoise should be used only in situations where the color channels are damaged
- Std Denoise
- Method
- Median Classical/Center Weighted median box method, good for impulse noise. Center weighted median gives more weight to the central pixel, thus preserving it.
- Radius >= 1. Greater radius less details preserved
- Center weight >= 1. Greater weight means more details preserved (CWM).
- Gauss (Std/Bilateral) Classical gauss and bilateral (sometimes is useful for high noise which is difficult to remove with other methods or to soften the image).
- Spatial Sigma Sigma of the gauss kernel applied. Greater sigma means more pixels taken into account and more blurring.
- Range sigma Sigma of the gauss kernel applied to the color nearer pixels. Greater sigma means more pixels taken into account and more blurring. For classical gauss set it to 0.
- Wavelets (DWT) Overcomplete wavelets. Slow with Q3.
- Noise sigma Greater sigma means more denoising.
- Mode VisuShrink Soft / VisuShrink Hard / BayesShrink Soft / BayesShrink Hard. Soft threshold means more blur but usually gives better visual results.
- Quality More quality means less artifacts, more blur and more time
- Wavelets (CWT) Complex wavelets give better results than overcomplete wavelets, but the result can't be as blurred as it can be with overcomplete ones.
- Noise sigma Greater sigma means more blurring.
- Mode VisuShrink Soft / VisuShrink Hard. Soft threshold means more blur but usually gives better visual results.
- DCT The best method along with NLM. Slow.
- Noise sigma Greater sigma more blurring
- Size Size of the DCT block. Usually greater values give better results.
- NLM Non local means. The best method along with DCT.
- Spatial sigma Higher sigma more denoise.
- Learn radius Size of the pixel rectangle taken into account for comparisons. Sometimes greater is better and sometimes not. Greater values means greater processing time
- Compare radius Size of the pixel rectangle, around each point in the learn rectangle, compared
- Enhanced Gives better results on plain color areas (slower than standard)
- Conservative Preserve more than standard
- Anisotropic diffusion This method is more focused on denoise preserving image features than in visual quality.
- Conductance More conductance means less detail preservation
- Iterations More iterations means less detail preservation
- Mode Curvature/Gradient
- Apply to Channel The algorithm could be applied or not to each of the colorspace channels. For instance for color noise, use YCbCr and apply only to Cb and Cr
- Preserve noise Only modify pixels which differs from original values more than the threshold. This blend mode can be used for two purposes: to modify only pixels which can be considered outliers (when there are impulse noise) , or to maintain some noise and give the image a more natural look.
- Color Denoise
- Method
- Spatial sigma Higher sigma more denoise.
- Learn radius Size of the pixel rectangle taken into account for comparisons. Sometimes greater is better and sometimes not. Greater values means greater processing time
- Compare radius Size of the pixel rectangle, around each point in the learn rectangle, compared
- Enhanced Gives better results on plain color areas (slower than standard)
- Conservative Preserve more than standard
- Apply to Channel The algorithm could be applied or not to each of the colorspace channels. For instance for color noise, use YCbCr and apply only to Cb and Cr
|
|